Socialist Vermont Sen. Bernie Sanders speaks during a rally in Boston in October. (Photo: Darren McCollester/Getty Images)
While there are many things I admire about Scandinavian nations, I’ve never understood why leftists such as Bernie Sanders think they are great role models.
Not only are income levels and living standards higher in the United States, but the data show that Americans of Swedish origin in America have much higher incomes than the Swedes who still live in Sweden. And the same is true for other Nordic nations.

The Nordics-to-Nordics comparisons seem especially persuasive because they’re based on apples-to-apples data. What other explanation can there be, after all, if the same people earn more and produce more when government is smaller?
The same point seems appropriate when examining how people of Chinese origin earn very high incomes in Hong Kong,Singapore, Taiwan, and the United States (all places with reasonably high levels of economic liberty), but are relatively poor in China (where there is still far too much government control over economic affairs).
Again, what possible explanation is there other than the degree of economic freedom?
 Let’s now look at two other examples of how leftist arguments fall apart when using apples-to-apples comparisons.
Let’s now look at two other examples of how leftist arguments fall apart when using apples-to-apples comparisons.
A few years ago, there was a major political fight in Wisconsin over the power of unionized government bureaucracies. State policy makers eventually succeeded in curtailing union privileges.
Some commentators groused that this would make Wisconsin more like non-union Texas. And the Lone Star States was not a good role model for educating children, according to Paul Krugman.
This led David Burge (a.k.a., Iowahawk) to take a close look at the numbers to see which state actually did a better job of educating students. And when you compare apples to apples, it turns out that Longhorns rule and Badgers drool.
…white students in Texas perform better than white students in Wisconsin, black students in Texas perform better than black students in Wisconsin, Hispanic students in Texas perform better than Hispanic students in Wisconsin. In 18 separate ethnicity-controlled comparisons, the only one where Wisconsin students performed better than their peers in Texas was 4th grade science for Hispanic students (statistically insignificant), and this was reversed by 8th grade. Further, Texas students exceeded the national average for their ethnic cohort in all 18 comparisons; Wisconsinites were below the national average in 8… Not only did white Texas students outperform white Wisconsin students, the gap between white students and minority students in Texas was much less than the gap between white and minority students in Wisconsin. In other words, students are better off in Texas schools than in Wisconsin schools – especially minority students.
This is what I call a devastating debunking.
Though Krugman routinely invites mockery, and I’ve enjoyed exposing his disingenuous, sloppy, and dishonest use of data on issues such as Obamanomics,California jobs, American fiscal policy, Greek economics, U.S. and U.K. austerity,German fiscal policy, Estonian economics, British fiscal policy, inflation, European austerity, the financial crisis, and the Heritage Foundation.
Gee, with all these examples, I wonder if there’s a pattern?
Our second example showing the value of apples-to-apples comparisons deals with gun control.
Writing for PJ Media, Clayton Cramer compares murder rates in adjoining American states and Canadian provinces. he starts by acknowledging that a generic US-v.-Canada comparison might lead people to think gun rights are somehow a factor in more deaths.
…for Canada as a whole, murder rates are still considerably lower than for the United States as a whole. For 2011, Canada had 1.73 homicides per 100,000 people; the United States had 4.8 murders and non-negligent homicides per 100,000 people.
But he then makes comparisons that suggest guns are not a relevant factor.
…look at murder rates for Canadian provinces and compare them to their immediate American state neighbors. When you do that, you discover some very curious differences that show gun availability must be either a very minor factor in determining murder rates, or if it is a major factor, it is overwhelmed by factors that are vastly more important.
Gun ownership is easy and widespread in Idaho, for instance, but murder rates are lower than in many otherwise similar Canadian provinces.
I live in Idaho. In 2011, our murder rate was 2.3 per 100,000 people. We have almost no gun-control laws here. You need a permit to carry concealed in cities, but nearly anyone who may legally own a firearm and is over 21 can get that permit. We are subject to the federal background check on firearms, but otherwise there are no restrictions. Do you want a machine gun? And yes, I mean a realmachine gun, not a semiautomatic AR-15. There is the federal paperwork required, but the state imposes no licensing of its own. I have friends with completely legal full-automatic Thompson submachine guns. Surely with such lax gun-control laws, our murder rate must be much higher than our Canadian counterparts’ rate. But this is not the case: I was surprised to find that not only Nunavut (21.01) and the Northwest Territories (6.87) in Canada had much higher murder rates than Idaho, but even Nova Scotia (2.33), Manitoba (4.24), Saskatchewan (3.59), and Alberta (2.88) had higher murder rates.
The same is true for other states (all with laws that favor gun ownership) that border Canada.
What about Minnesota? It had 1.4 murders per 100,000 in 2011, lower than not only all those prairie provinces, but even lower than Canada as a whole. Montana had 2.8 murders per 100,000, still better than four Canadian provinces and one Canadian territory. When you get to North Dakota, another one of these American states with far less gun control than Canada, the murder rate is 3.5 per 100,000, still lower than Manitoba, Saskatchewan, the Northwest Territories, and Nunavut. And let me emphasize that Minnesota, Montana, and North Dakota, like Idaho, are all shall-issue concealed-weapon permit states: nearly any adult without a felony conviction or a domestic violence misdemeanor conviction can obtain a concealed weapon permit with little or no effort.
The takeaway from this evidence (as well as other evidence I have shared) is that availability of guns doesn’t cause murders.
Other factors dominate.
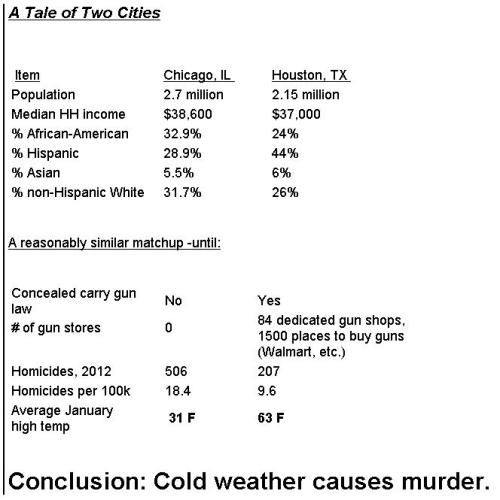
P.S. Regarding the gun control data shared above, some leftists might be tempted to somehow argue that American states with cold weather somehow are less prone to violence. That doesn’t make sense since the Canadian provinces presumably are even colder. Moreover, that argument conflicts with this bit of satire comparing murder rates in chilly Chicago and steamy Houston.
P.P.S. In his role as Iowahawk, David Burge has produced some great political satire, including extortion by Obama’s teleprompter, the bible according to Obama, mockery of theObama campaign’s life-of-Julia moocher, and (my favorite) the video about a government-designed car.